Human Reproduction - Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper 01
Ch-3 Human Reproduction
- Which of the following group of hormones are produced during pregnancy?
- Progestogenes, hPL and relaxin
- hCG, hPL and relaxin
- Estrogens, hPL and relaxin
- hCG, estrogens and relaxin
- Which one is correctly matched pair
- Colostrum : secretion found in seminal fluid
- Clitoris : male external gene
- Coitus : Sexual intercourse
- Ovary : pigmented circular area around the nipple
- In human beings, fertilization of egg takes place in
- Ovary
- Oviduct
- Vagina
- Uterus
- Five oogonia yield 10 primary oocytes, then how many ova are produced on completion of oogenesis?
- 40
- 20
- 5
- 10
- Failure of testes to descend into scrotum is called
- Archentronism
- Testinolism
- Cryptochidism
- Copulation
Androgens are produced by Sertoli cells.(True/False)
Some organisms like honey bees are called parthenogenetic animals. (Give reason)
Which part in the male reproductive system stores sperms?
Leydig cells are found in ovary. .(True/False)
Write the location and function of the sertoli cells in humans.
Name the hormone responsible for the descent of testes into the scrotum. Why does the failure of the process result in sterility?
Study the following flow chart Name the hormones involved at each state. Explain their functions.
Draw a labeled diagram of male reproductive system.
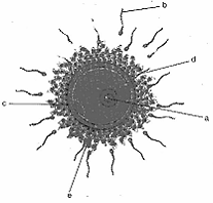
Study the illustration given below and
- Identify 'a'
- Name and state the function of 'c'.
- Identify 'd'
- Explain the role of hormones in the formation and releases of 'a'
- Draw a diagram of 'b' separately and label the parts:
- that helps its entry into 'a'
- that carry genetic materials
- that helps in its movement.
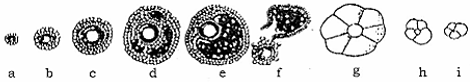
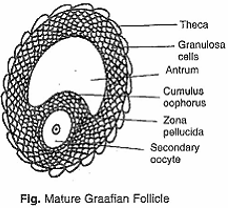
- Identify the figure that illustrates corpus luteum and name the pituitary hormone that influences its formation.
- Specify the endocrine function of corpus luteum. How does it influence the uterus? Why is it essential?
- What is the difference between 'd' and 'e'?
- Draw a neat labelled sketch of Graafian follicle.
CBSE Test Paper 01
Ch-3 Human Reproduction
Answer
- hCG, hPL and relaxin, Explanation: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogens (hCL) and relaxin are produced in human females only during pregnancy.
- Coitus : Sexual intercourse, Explanation: Transfer of male gamete into female genital tract takes place during sexual intercourse, which is also called as coitus. Clitoris is the part of female reproductive system, colostrum is first milk secreted from mammary gland.
- Oviduct, Explanation: Fertilisation of egg in human female takes place in oviduct or fallopian tube at the junction of ampullar-isthamus. Fertilized egg travels towards the uterus after that.
- 5, Explanation: Each oogonium produces one ovum at the end of oogenesis process and three polar bodies. Thus, five oogonia will produce five ova at the completion of oogenesis process.
- Cryptochidism, Explanation: Cryptochidism is an abnormal condition in male reproductive system in which scrotum does not descend outside the abdominal condition. The males may be not able to produce fertile sperm.
- False; Androgens are produced by Leydig cells found in seminiferous tubules of the testis.
- In honey-bees, ovum grows and matures into an individual without fertilization. Therefore these animals are called as parthenogenetic animals.
- The epididymis is a long, coiled tube that stores sperm and transports it from the testes.
- False; Leydig cells are found in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
- Sertoli cells are large, pyramid shaped found inside the seminiferous tubules.
Functions. its main function is to nourish the developing sperm cells through the stages of spermatogenesis, the Sertoli cell has also been called the "mother" or "nurse" cell. Sertoli cells also act as phagocytes, consuming the residual cytoplasm during spermatogenesis. - AMH, Androgens, Panacrine hormone, Gonadotrophins and Testesterone contribute to the descending of testes into the scrotum. Gonadotrophins acts on leydig cells which in turns stimulates the production of testerone which plays a major role in descent of testes from the scrotum.
The failure of the testes to descend into the scrotum causes sterility because sperm formation does not occur at the abdominal temperature. The human male possesses two testes lying in a scrotum outside the abdominal cavity. Sperm production is efficient at a temperature that is lower than the body temperature. Scortum acts as a thermoregulator and enhances the sperm production by keeping the testes cool - Hypothalamus: It releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which stimulates pituitary.
Pituitary: After stimulation, it secretes FSH and LH. FSH regulates the functioning of the ovary during follicular phase by stimulating the growth of an ovarian follicle into mature graaffian follicle and secretion of oestrogens from the follicle cells. LH stimulates the mature follicle to rupture and release the ovum(ovulation).
Ovary: After ovulation LH stimulates the formation of corpus luteum inside the ruptured follicle.
Pregnancy: Corpus luteum starts secretion of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of pregnancy. 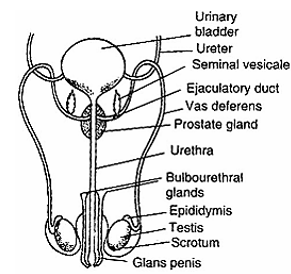
- Human ovum
- Zona pellucida. When one sperm penetrates the ovum, the zona pellucida makes it impervious to other sperm
- Cells of corona radiate layer.
- GnRH of Hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and LH.
- FSH stimulates the formation of ovum by stimulating the growth of ovarian follicles.
- By the action of LH the oocyte completes the first meiotic division and becomes secondary oocyte and finally release from the follicle. 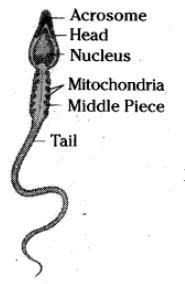
- Figure 'g' illustrates corpus luteum - Luteinizing hormone
- Corpus luteum secretes progesterone hormone, which stimulates the continued growth of the superficial layer of endometrium and endometrium becomes ready for implantation. - It is essential for the continuation of pregnancy.
- The figure 'd' represents fertiary follicle in which primary oocyte completes its first meiotic division, while figure 'e' represents the mature follicle (Graafian follicle) ready for ovulation.