Biotechnology and its Applications - Solutions
CBSE Class 12
Biology
Ch 12 – Biotechnology and Its Applications
1. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because
(a) Bacteria are resistant to the toxin.
(b) Toxin is immature.
(c) Toxin is inactive.
(d) Bacteria enclose toxin in a special sac.
Ans. (c) Toxin is inactive. In bacteria, the toxin is present in an inactive form called prototoxin. This gets converted into the active form when it enters the salivary gland of insects having alkaline medium.
2. What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Ans. Transgenic bacteria are bacteria in which a foreign gene is introduced into its genome. For example, two DNA sequences coding for A and B chains of human insulin introduced into the plasmid of E. coli start producing insulin chains.
3. Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Ans. Advantages of GM crops:
(i) Genetic modification has made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, heat, salt).
(ii) Viral resistance can be introduced.
(iii) Over ripening losses can be reduced. Example: Flavr Savr tomato
(iv) Enhanced nutritional value of food. Example: Golden Rice
(v) Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides.
Disadvantages of GM crops:
(i) Transgenes in crop plants can endanger native species. Example: The gene for Bt toxin expressed in pollen may end natural pollinators such as honey bees.
(ii) Weeds also become resistant.
(iii) Products of transgenes may be allergic or toxic.
(iv) They cause damage to the natural environment.
4. What are Cry proteins? Name an organism which produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Ans. Cry proteins are toxic proteins (insecticidal proteins) secreted by Bacillus thuringiensis in crystal form during a particular phase of their growth. The toxin is coded by a gene called cry.
The genes encoding cry proteins called Bt toxin genes were isolated from B. thuringiensis and incorporated into several crop plants such as Bt cotton, Bt corn etc. to provide resistance against insect pests.
5. What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Ans. It is a collection of methods which allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child or embryo. In gene therapy, normal genes are inserted into a person's cells or tissues to treat a hereditary defect. Gene therapy is being tried for sickle cell anaemia and severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
In some children, ADA deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation. In others, it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to the patient by injection. However, both of these approaches are not completely curative.
In gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in culture outside the body. A functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes, which are subsequently returned to the patient. Because these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. However, if the gene isolated from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, the disease could be cured permanently.
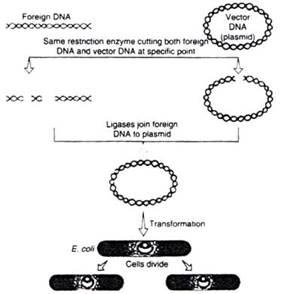
6. Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Ans.
7. Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Ans. Oil is a lipid synthesised by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol with three molecules of fatty acids. Thus, the oil from the seeds can be removed by preventing the synthesis of either glycerol or the enzyme lipase which catalyses the synthesis of oil. It can be achieved by knocking out the genes coding for the enzyme lipase or the enzyme required for the synthesis of glycerol.
8. Find out from the internet what is golden rice.
Ans. Golden rice is a variety of rice produced through genetic engineering to biosynthesize beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A, in the edible parts of rice. It is intended to produce a fortified food to be grown and consumed in areas with a shortage of dietary vitamin A.
9. Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Ans. No. Human blood does not have the enzymes nucleases and proteases. In human beings, blood serum contains different types of protease inhibitors, which protect the blood proteins from being broken down by the action of proteases. The enzyme nuclease catalyses the hydrolysis of nucleic acids which are absent in blood.
10. Consult the internet and find out how to make an orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Ans. For making any oral drug or nutritional supplement, the action of digestive enzymes has to be taken into account. Most of the antibiotics and vitamin supplements are made in capsule form to prevent the action of HCl in the stomach. For protein preparation, the major source is groundnut shells. The protein extracted from the source is predigested so as to make it absorbable by the digestive system.